Removal of physical impurites:
There are several methods for the removal of physical impurities of water some methods are as follows.
- Screening
- Sedimentation or settling
- Coagulation
- Filteration
- Reverse osmosis
Screening:
In screening process water is passed through screens or series of screens which results in removal of floating metals.
Sedimentation or settling:
Waste particles are removed by the action of gravity. Gravity causes most of the suspended coarse particles such as clay,sand,bacteria to fall to the bottom of the sedimentation or settling tank from there they are removed.
SEDIMENTATION TANK
Co-Agulation:
Such particles take longer time to settle to remove such particles coagulant is added. Coagulant is a chemical that combines with the smaller particles in water to form large particles.Most commonly coagulatnt is Alum.
COAGULATION
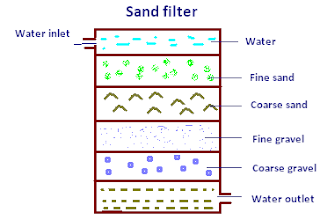
Filteration:
In filteration water is passed through sand filters which results in removal of clay, sand also bacteria.there are two types of sand filters.
FILTERATION
a.Gravity filters:
Generally used for munciple water treatment and to less extent for industrial water treatment.In tank consisting of layers of fine sand,coarse and gravel,raw water enters from one part of tank leaving sand on gravity filter from the top and clean water is taken from the bottom .Working period is 24 hrs.
b.Pressure filters:
They are used for industrial water treatment, Pressure filter is the tank having raw water inlet from the top and passes through the layers of gravel and sand. Main advantage of pressure filter is that when filteration action is lowered we don't replace sand and grave.Working period is 32 hours.